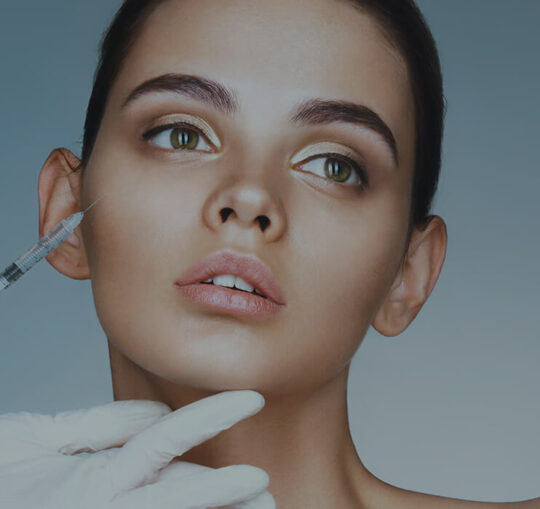
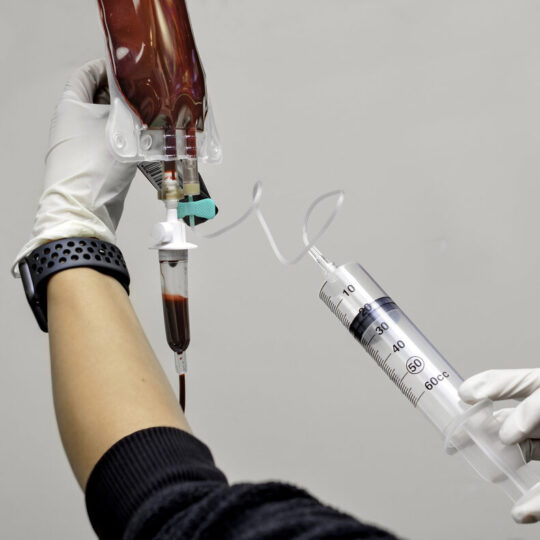
Chelation
It is based on the chelation process, in which chemicals are used to remove heavy metals and other substances from the body. Although chelation was originally used to treat conditions such as lead poisoning, chelation therapy is now claimed to protect against heart disease and other major health problems. (Autism, Alzheimer’s disease, Band keratopathy, Multiple sclerosis, Peripheral arterial disease, etc.)
In the therapy, a chelating agent is introduced into the body through an intravenous (IV) drip or an oral pill. Once it enters the bloodstream, the agent binds to certain molecules (such as metals or minerals) and is eliminated from the body through urine, taking those molecules with it. One of the most common chelating agents used in therapy is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). EDTA is known to remove substances such as lead, iron, copper and calcium from the blood.

More treatments

HOME

in the procedures.

treatments

of life.
We offer a wide range of services, from aesthetic medicine to functional and orthopedic medicine, all supported by cutting-edge regenerative medicine technologies. This combination of specialties positions us as the first clinic of its kind in Ciudad Juárez, providing a comprehensive and innovative approach to healthcare.
https://youtu.be/UUUbyz9x0vc
First multidisciplinary clinic in Ciudad Juárez that includes regenerative medicine in its procedures.
ARCOSE BIOMEDICAL CENTER














Our Treatments
Infiltracion de células madre en disfunción eréctil
Ozonoterapia
Filler
We offer virtual and in-person consultations.
Orthopedic
Functional Nutritional
Functional medicine
Lo que dicen nuestros pacientes
“Me sometí a un tratamiento de medicina estética en Arcose Biomedical Center, y los resultados superaron todas mis expectativas. El personal fue muy amable y profesional, y el doctor me hizo sentir cómodo durante todo el proceso. La clínica es hermosa y moderna, y estoy ansioso por volver para otro tratamiento en el futuro.”
Ricardo PereaPaciente
“Recomiendo altamente Arcose Biomedical Center a cualquiera que busque tratamientos de medicina ortopédica y funcional. El personal es muy experimentado y conocedor, y el doctor me ayudó a entender todos los aspectos de mi tratamiento. Me siento mucho mejor y más cómodo después de mi tratamiento, y estoy muy agradecido por la atención excepcional que recibí en la clínica”
Anna JohnsonPaciente
“Después de lidiar con dolor de rodilla por años, finalmente decidí buscar tratamiento en Arcose Biomedical Center. El personal fue muy atento y me ayudó a entender todos los aspectos de mi tratamiento de medicina ortopédica y funcional. El doctor fue muy conocedor y experimentado, y me hizo sentir cómodo durante todo el proceso. Ahora puedo caminar sin dolor y estoy muy agradecida”
Patricia SosaPaciente
“Fui para un tratamiento de medicina estética y quedé impresionada por la atención que recibí. Desde el momento en que entré, el personal me hizo sentir muy cómoda y bienvenida. El doctor fue muy amable y profesional, y me explicó todo el procedimiento antes de comenzar. ¡Los resultados fueron espectaculares y no puedo esperar para volver!”
Sofia GuzmanPaciente
![]()







![]()

Patient evolution – Facial rejuvenation
Before
After

Get the latest news
All our services are carefully thought out in the restoration and care of the most important element, you!
Terapia Celular: Células Madre Mesenquimales.
December 29, 2023
The Secrets to Building Strong Professional Relationships
January 1, 2024
Maximizing Productivity in a Remote Work Environment
January 1, 2024
Balancing Work and Life: Strategies for Professionals
January 4, 2024
Innovative Approaches to Problem-Solving in the Workplace
January 1, 2024Read More
Share
Aumento de labios con ácido hialurónico
January 1, 2024
The Secrets to Building Strong Professional Relationships
January 2, 2024
Maximizing Productivity in a Remote Work Environment
December 29, 2023
Balancing Work and Life: Strategies for Professionals
January 1, 2024
Innovative Approaches to Problem-Solving in the Workplace
January 3, 2024Read More
Share
Inflamación, hormonas y salud: Navegando la conexión compleja.
January 2, 2024
The Secrets to Building Strong Professional Relationships
December 29, 2023
Maximizing Productivity in a Remote Work Environment
January 1, 2024
Balancing Work and Life: Strategies for Professionals
December 30, 2023
Innovative Approaches to Problem-Solving in the Workplace
December 30, 2023Read More
Share
Get in contact with us